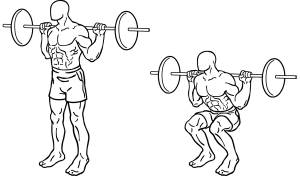
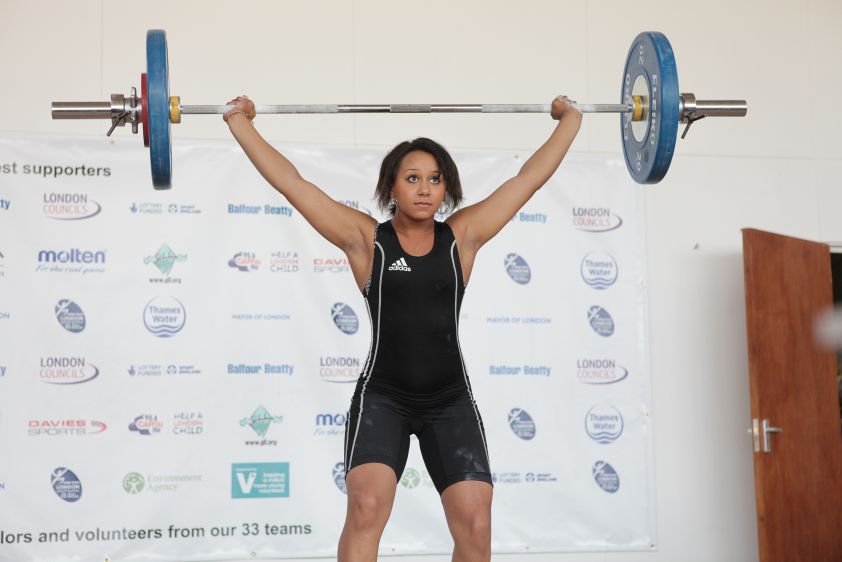
Squats are a great exercise to strengthen the lower body and are fairly easy to incorporate into a workout. However, as with most athletic and weight-lifting activities, form is incredibly important in completing the exercise correctly. Improper form can result in injury or a lack of effectiveness, and no one wants to get hurt or waste his or her time working out incorrectly.
Squats can be particularly difficult to figure out the correct form because there is some debate over how to position the body. Some people believe that a wider stance is more effective, while others think that the feet should be shoulder-width apart.
Aside from that, many disagree on how deep squats should go—is parallel good enough, or should a squatter try to get the deepest squat possible? All of these conflicting opinions can be confusing, but squats are actually fairly easy to sort out.
Figuring out Squat Stance
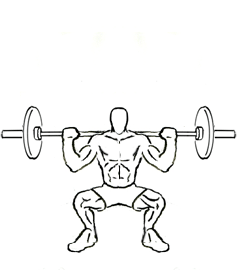
Positioning the legs in the first step in a successful squat. First of all, stance depends on the physical composition of the person exercising. Some people may be more comfortable with a wider stance, and women in particular may choose a wide stance or point their feet out more because their hips are turned out further. Having a wide stance does not necessarily mean that the squat is being done incorrectly.
The most important part is choosing a stance that allows for proper form. Keeping the feet closer to shoulder distance apart will work the legs and quads more, while a wider stance is better for working out the glutes. Either of these choices is fine, depending on which area of the body you want to work harder. The most important aspects are keeping the torso in the correct position, keeping your feet firmly planted on the floor, tracking your knees and feet in the same direction, and making sure your knees do not extend past your toes.
How Low Should You Go?
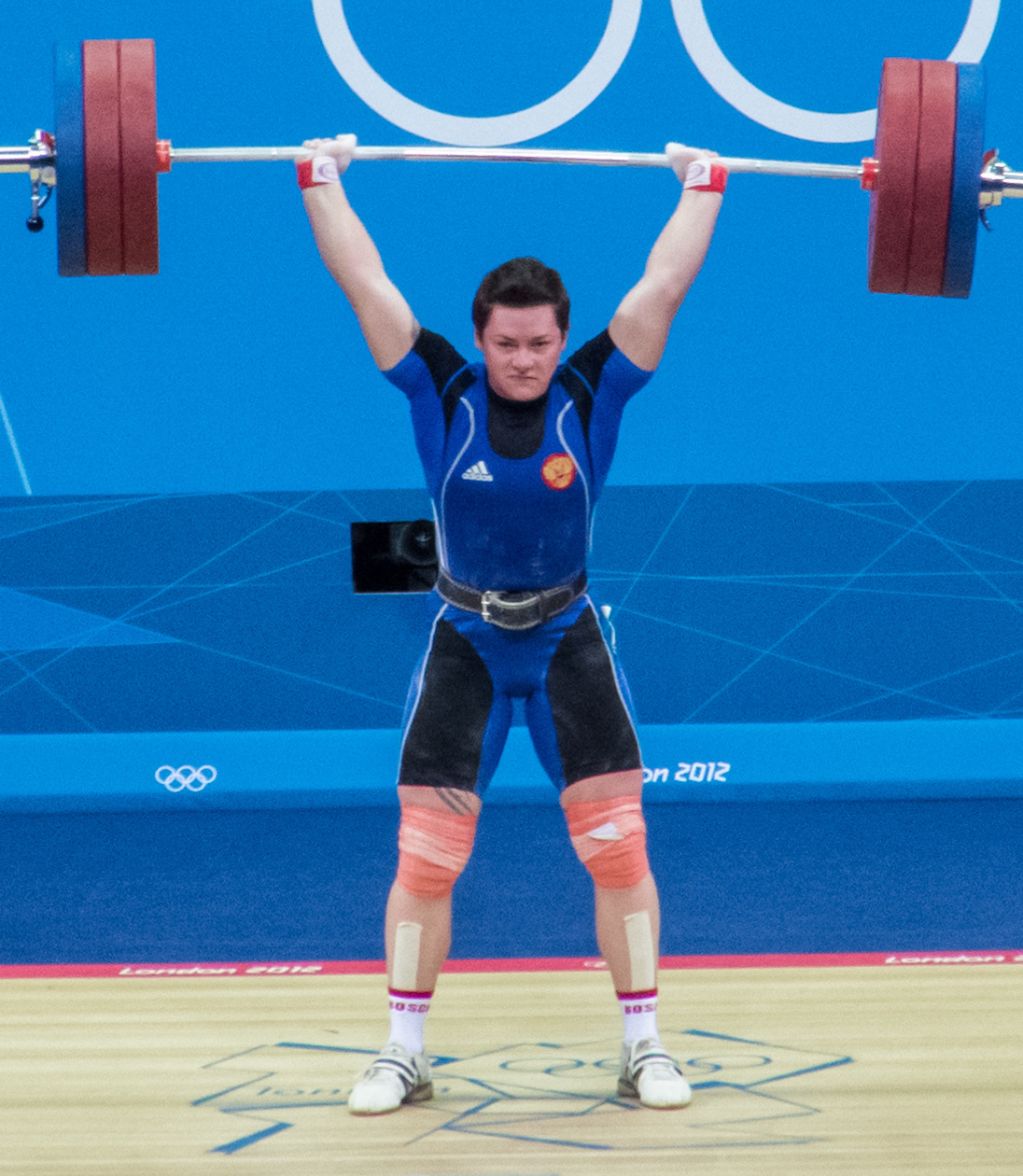
While it is a popular opinion that “real” squats require lowering the body to the ground, this is not necessary for an effective squat. The key with squats is to go below parallel—to have the line of the hips go beneath the line of the knees (unless you have a medical condition that prevents this). Deeper squats are not necessarily more successful, and in some cases may be a detriment [1]. Once again, the key is keeping correct form.
Sacrificing form for a deeper squat means that the exercise is not as effective as it would be with a shallower squat and perfect form. Letting the knees splay out or cave in, putting too much pressure on the toes, or bending the lower back can all result in injury. It’s best to stay comfortable with your stance and depth, rather than trying for a wider or deeper squat and risking injury.
Getting the Most Out of Your Squats
When you have the correct form down, squats should be an effective way to build lower body strength and muscle. Once comfortable with squats, you may want to look into supplementing with branched-chain amino acids to improve performance and muscle gains [2]. These supplements can give your workout an extra kick, and help you see better results faster.
You may also find yourself struggling with muscle soreness after an intense lower-body workout. Try taking a citrulline malate supplement to reduce muscle soreness or protein powder to support your muscles with proper nutrition.











 If you feel like you are in an overtrained state, the first step is to simply recognize it. Of course, this is easier said than done in many cases. The key to knowing that you’re overtraining is the constant feeling of exhaustion and progress coming to an almost non-existent stand still. The possibility that you may be overtraining should seriously be considered if this is the case.
If you feel like you are in an overtrained state, the first step is to simply recognize it. Of course, this is easier said than done in many cases. The key to knowing that you’re overtraining is the constant feeling of exhaustion and progress coming to an almost non-existent stand still. The possibility that you may be overtraining should seriously be considered if this is the case.
